Fast Outline renders outlines by rendering an extruded version of an object behind the original object.
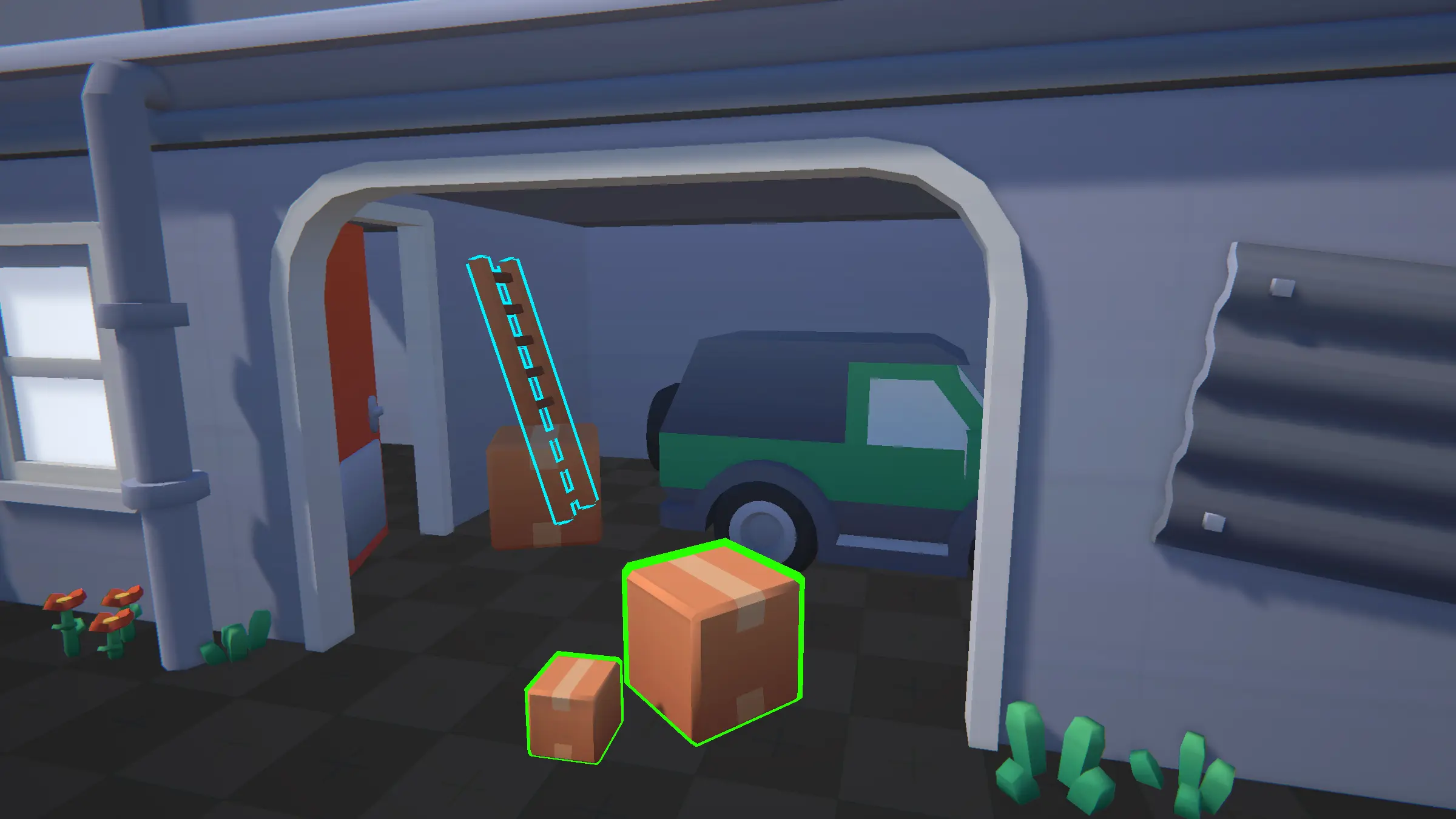

Advantages
- Performance: Not a screen-space effect, just re-renders the object with a simple shader.
- Object Exclusion: Easily select which specific objects should receive an outline.
- Multiple Styles: Different objects can have completely different outline styles.
Disadvantages
- Inner Lines: No inner lines are rendered. Only outlines.
- Artifacts: This method may produce artifacts (inconsistent line widths, gaps). These issues may be mitigated. See more information below in the Artifacts section.
Configuration
The Fast Outline Settings object contains the settings related to this outline effect. Here are all of the settings explained. In Unity, each setting also has a tooltip which shows more information.
General Settings The general settings apply to the outline effect as a whole (with all sub-outlines included).
| Setting | Description | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| Stage | Controls when the render pass executes. | |
| Show In Scene View | Sets whether to render the pass in the scene view. | |
| Force Clear Stencil | Force clear the stencil buffer after the render pass. | Should normally not be enabled, but can be used if you notice unexpected interactions between different effects. |
Outline Settings To add an outline, click on the Add Outline button. This will add an outline to the list. You can add as many outlines as you want. See the Performance section for more information about the impact of adding outlines.
Each outline in the list is applied to objects that belong to the specified Rendering Layer Mask. See Rendering Layer Masks for more information about how the layer system works.
The outline settings apply to a specific outline.
| Setting | Description | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| Layer | The rendering layer(s) which will get an outline rendered for them. | See Rendering Layer Masks for more information. |
| Render | For which occlusion states to render the outline. | See Occlusion States for more information. |
| Blend | How to blend the outline with the rest of the scene. | |
| Mask | The masking strategy that is used to only show the outline where needed. | |
| Color | The color of the outline. | |
| Occluded Color | The color of the outline when it is occluded. | |
| Method | The vertex extrusion method that is used. | |
| Scaling | How to scale the width of the outline. | |
| Width | The width of the outline. | |
| Min Width | The minimum width of the outline. |
Vertex Extrusion Methods
The Fast Outline effect renders outlines by rendering an extruded version of a mesh. There are 8 different options available that control how the mesh is extruded.
Each option below is shown in an extreme way with an big outline width. For a lot of methods, bigger widths will result in an outline with gaps.
Vertex Position (OS)
Move each vertex along the vertex position in object space.
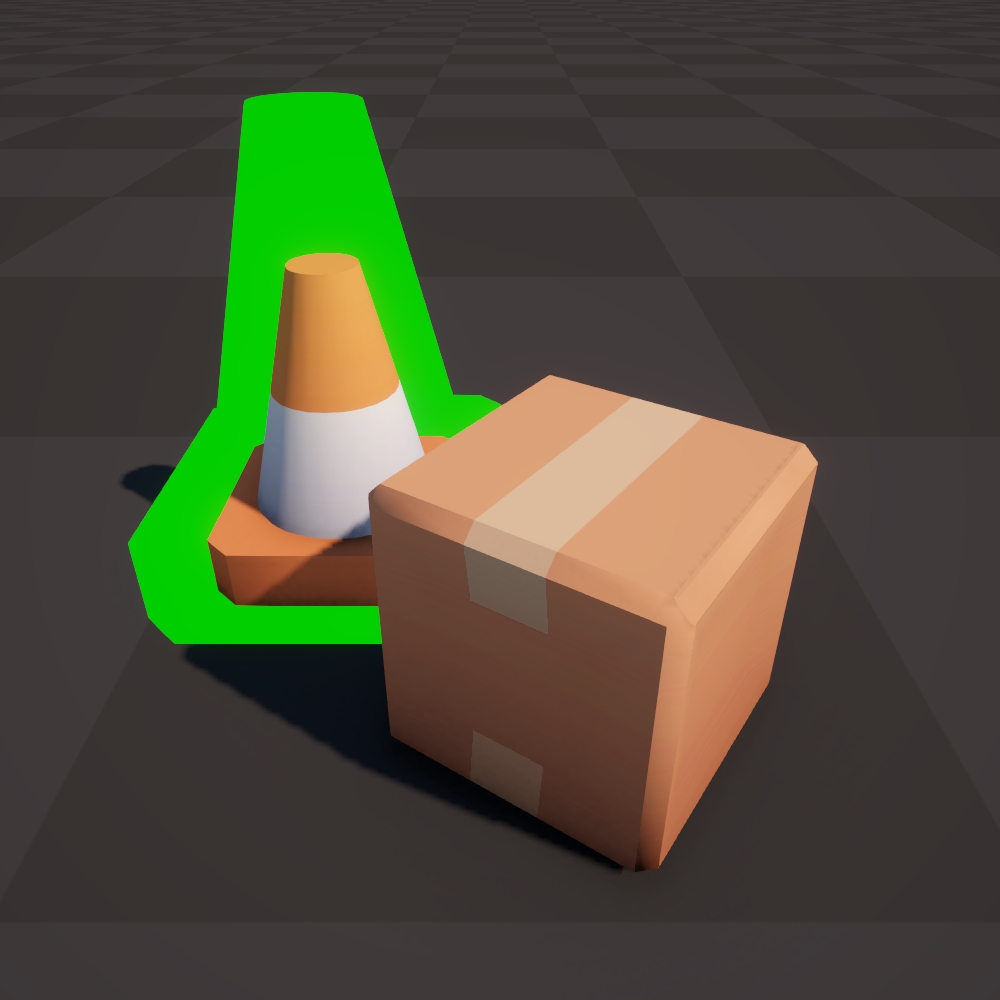

Normalized Vertex Position (OS)
Move each vertex along the normalized vertex position in object space.
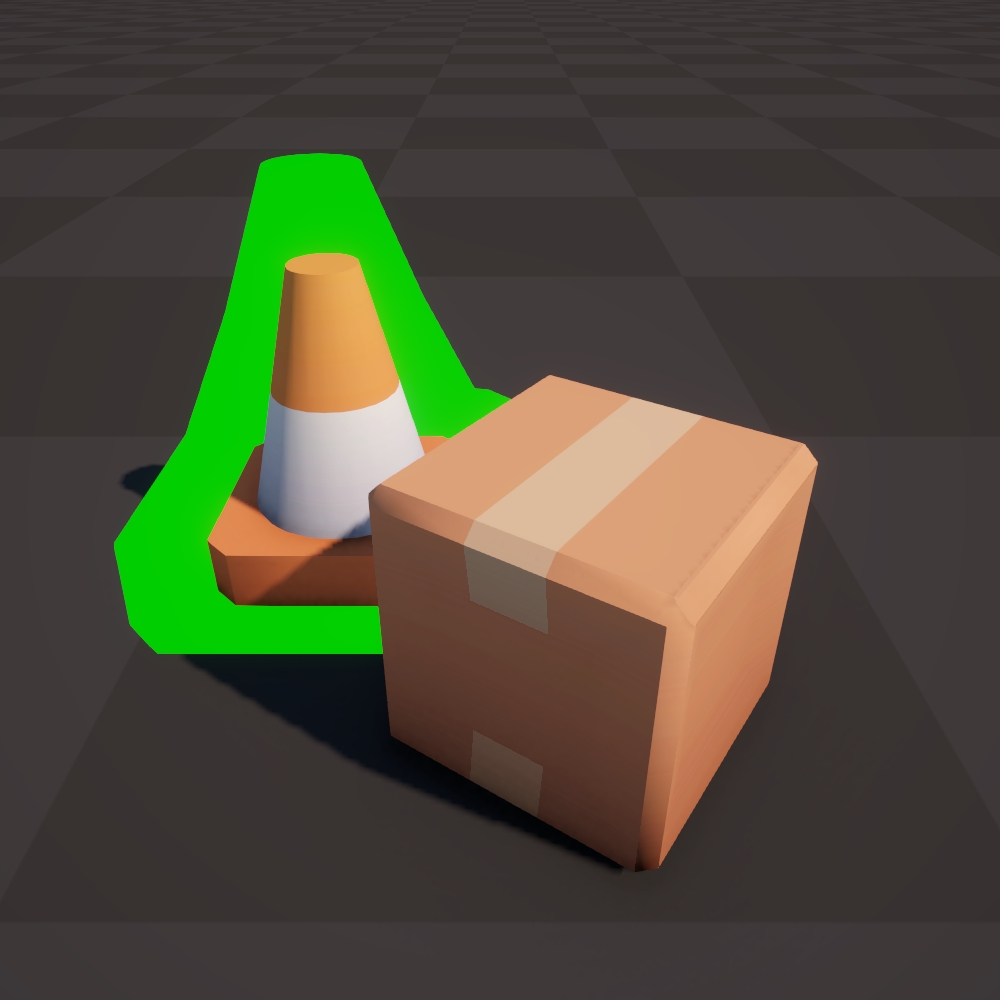

Normal Vector (OS)
Move each vertex along the normal vector in object space.
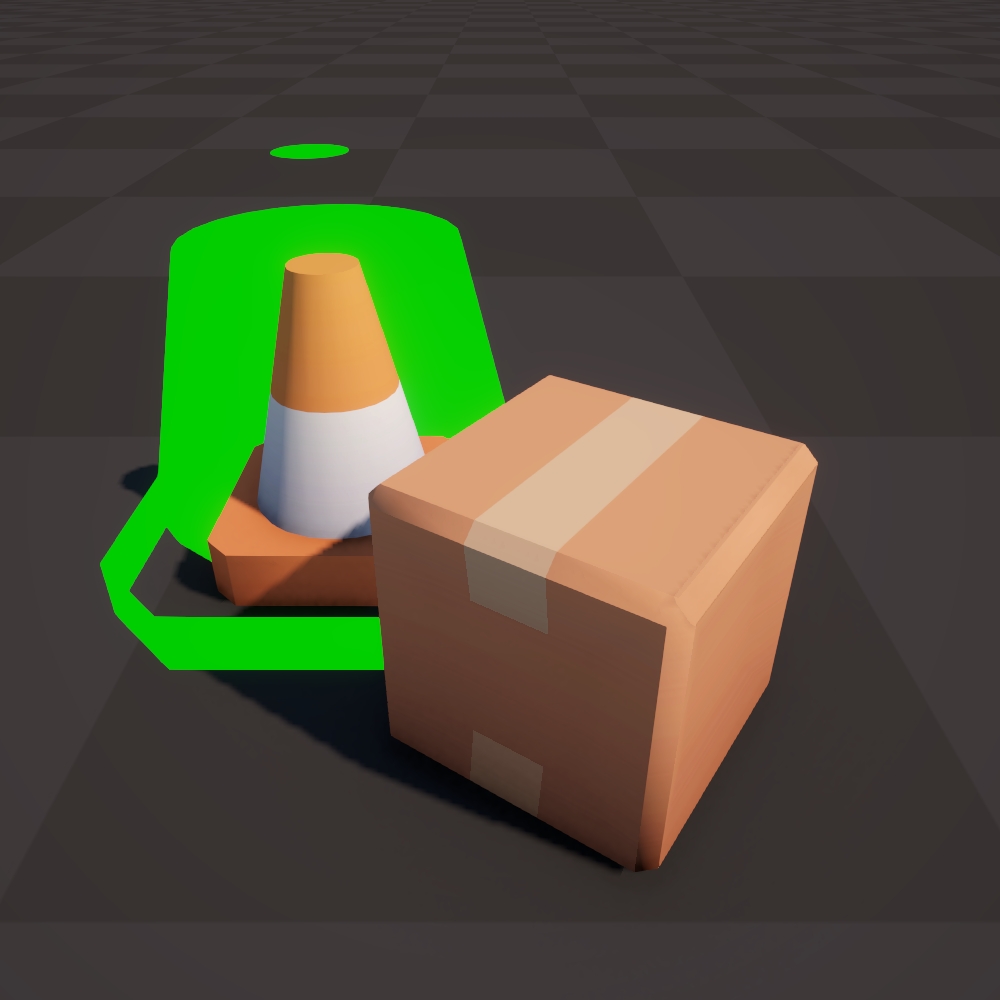

Vertex Color (OS) Move each vertex along the vertex color in object space.
Normal Vector (CS)
Move each vertex along the normal vector in clip space.
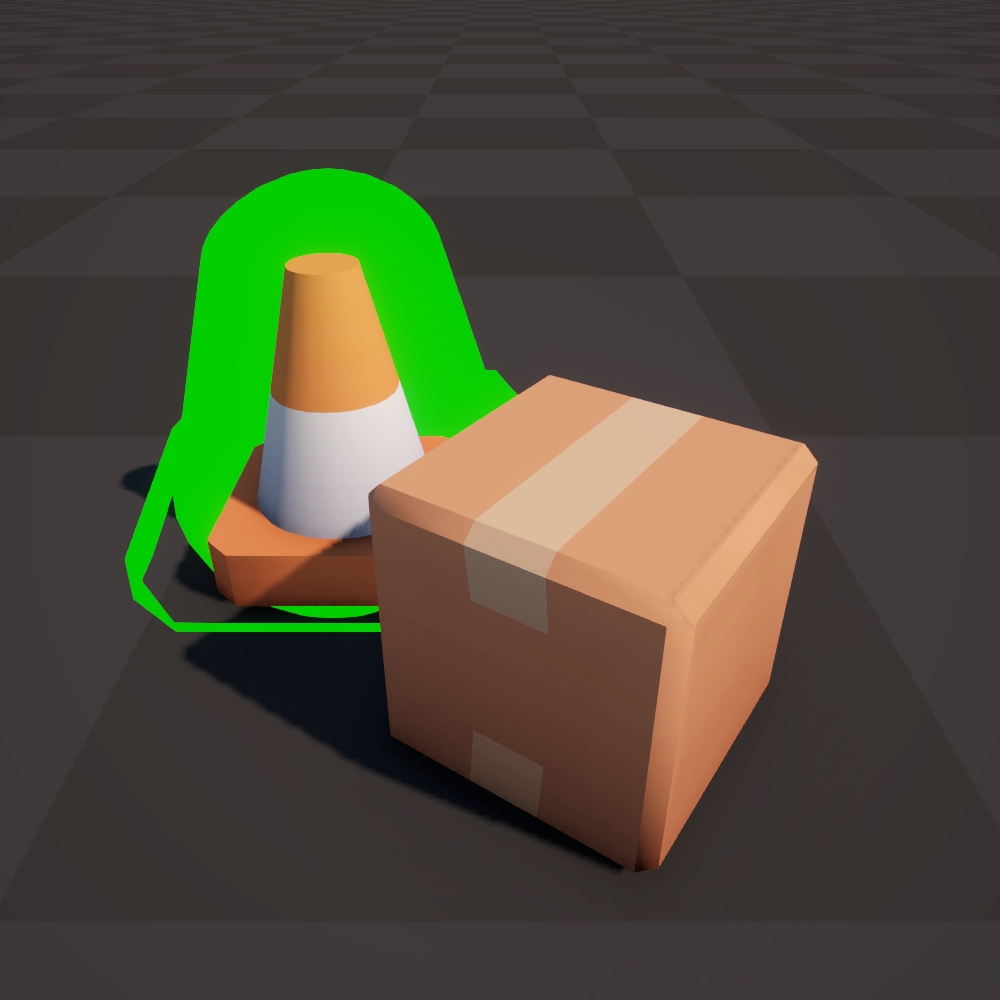

Normal Vector (SS)
Move each vertex along the normal in screen space.
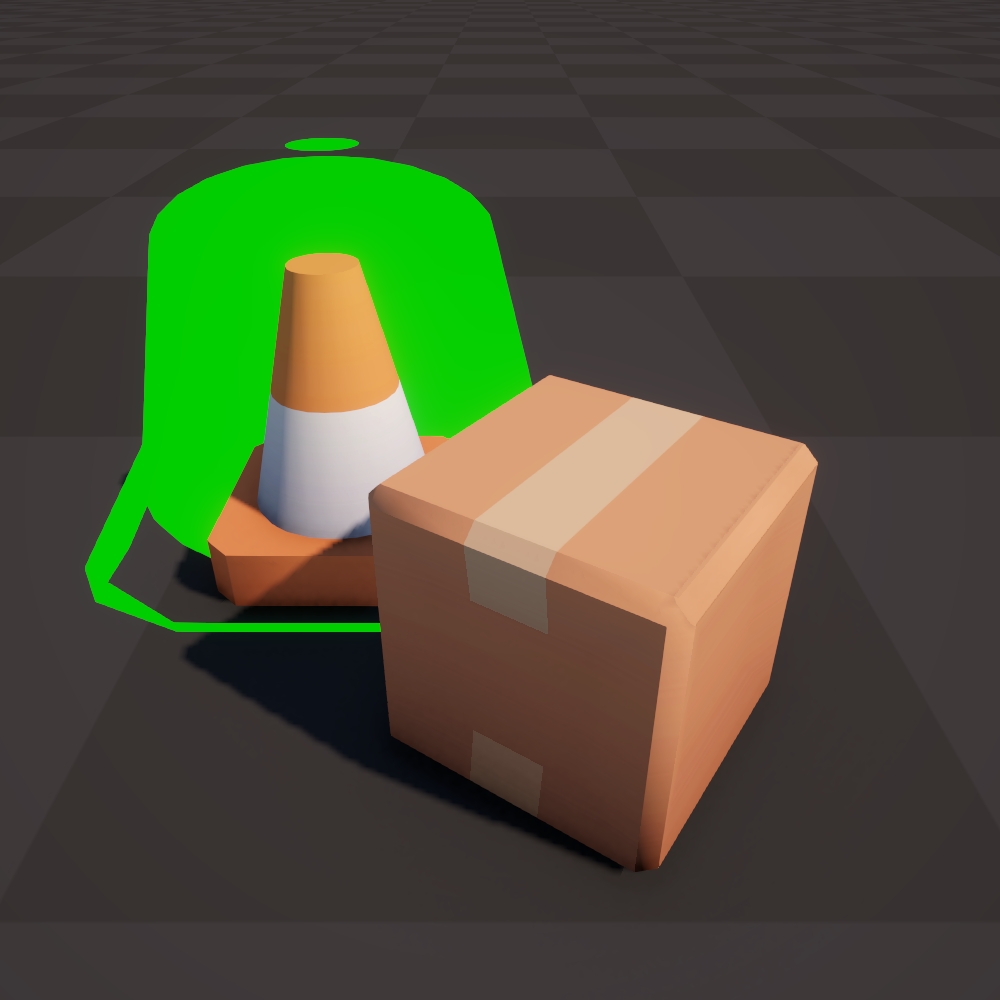

Normal Vector (WS)
Move each vertex along the normal in world space.
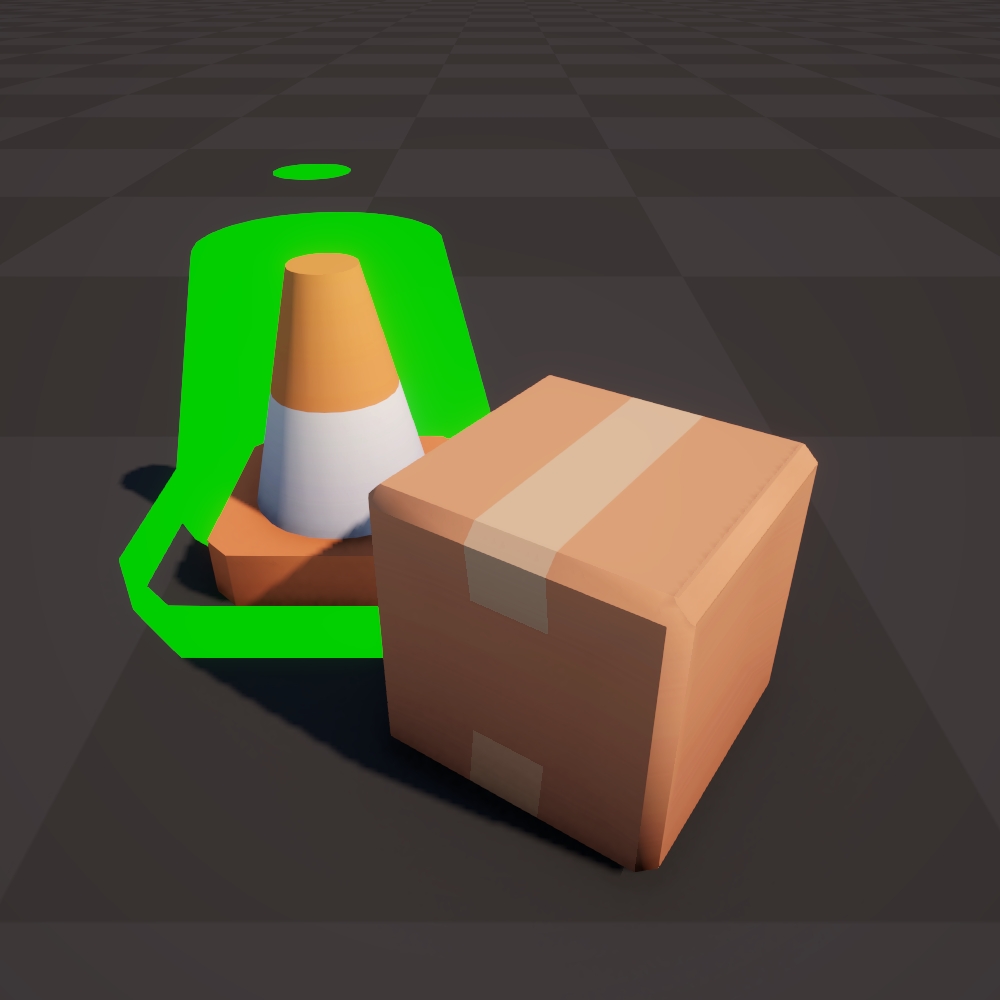

Baked Direction UV8 (OS) Move each vertex along the direction extracted from the UV8 channel in object space.
Scaling
The Fast Outline supports 2 methods of scaling the outline. Either the outline has a consistent screen-space width, or it is scaled by distance. The main difference will be when zooming out, when the object that is outline takes up a small space of the scene.
Constant The outlines will always take up the same width in terms of screen-space pixels. When zooming out, this may become disproportionally large compared to the smaller object it is outlining.
Scale With Distance The outlines will be reduced in size while zooming out. This will keep the outline the same size relative to the object it is outlining. You can also set a Minimum Width to keep the outlines from becoming so small that you can no longer see them.
Artifacts
The Fast Outline effect renders outlines by rendering an extruded version of a mesh. This extrusion step may show some artifacts. The reason is that each vertex of the mesh is moved in a certain direction in 3D space, but with different vertices moving in different directions, this may introduce gaps or sharp edges in the extruded mesh. The artifacts may be especially noticeable on meshes with sharp edges. There are several ways to mitigate these issues.
- Extrusion method: Try using a different extrusion method in the outline settings. Some extrusion methods may produce better results in your case.
- Normal vector smoothing: In your 3D modelling software you could smooth the normal vectors of your mesh. This should produce a smoother outline as well. If you don’t want to directly smooth the normal vectors of your mesh, you could store a smoothed version of the normal vectors in the vertex colours and use the Vertex Color Extrusion method in the outline settings.
Limitations
There are some known limitations that come with the implementation of the Fast Outline effect.